The typical human ear can sense acoustical energy in the 20 Hz - 20,000 Hz (or 20 kHz) range. The frequency (Hz = cycles per second) of energy perceived corresponds with a specific pitch.
An equalizer is a device designed boost or reduce a specific frequency range in the electrical signal.
HPF/LPF
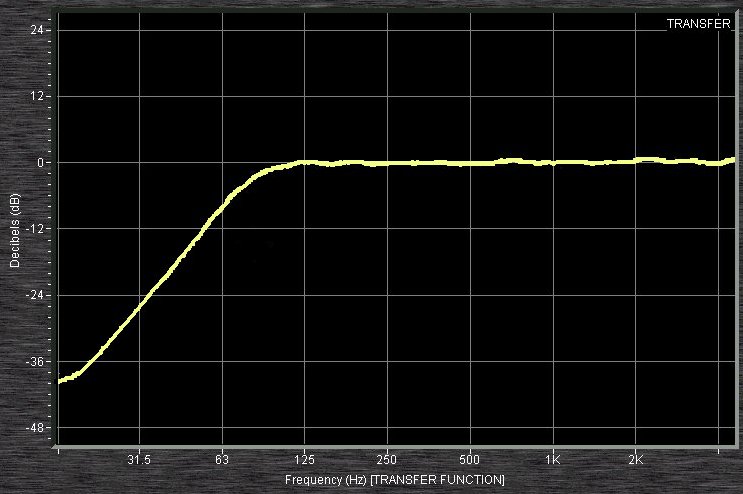
A high pass filter (a.k.a. low cut filter) will filter out all of the sonic information below a selected frequency, allowing the higher frequencies to "pass through."
A low pass filter (a.k.a. high cut filter) will remove all of the sonic information above a selected frequency, allowing all of the lower frequencies to "pass through."
Some HPF/LPFs will allow you to adjust the slope (dB/octave) around the selected frequency, allowing you to choose a more or less gradual range for the cutoff.
By Binksternet (Own work)
CC-BY-SA-3.0-2.5-2.0-1.0 or GFDL , via Wikimedia Commons
Shelf
A shelf EQ will adjust the gain of the selected frequency, and all frequencies above (or below) it. Some shelf filters will allow you to adjust the slope (dB/octave) around the selected frequency to create a more or less drastic adjustment.
Peak and Parametric
A peak EQ allows you to adjust the gain of a selectable frequency with a set bandwidth (or quality). A parametric EQ allows you to adjust the gain of a selectable frequency, and allows you to choose the bandwidth (or Quality) of the gain adjustment, allowing you to boost or reduce a narrow or broad range of the audio spectrum with one EQ. In the example below, the filter represented by the red line has a more narrow (higher value) bandwidth (quality), and adjusts a more precise section of the sound spectrum.
Graphic Equalizer (10-band or 31-band)
31-band graphic EQ's allow you to individually adjust the gain of 31 pre-selected frequencies (typically spaced 1/3 of an octave apart). Typically, these are used to compensate for problems within the room or the system.



